Air - Thermophysical Properties
Thermal properties of air at different temperatures - density, viscosity, critical temperature and pressure, triple point, enthalpi and entropi, thermal conductivity and diffusivity and more.
Thermophysical properties of air:
- Boiling temperature (at 1 bara): 78.8 K = -194.4 °C = -317.8 °F
- Bulk modulus elasticity : 1.01325 x 10 5 Pa or N/m 2
- Condensation temperature (at 1 bara): 81.8 K = -191.4 °C = -312.5 °F
- Critical temperature : 132.63 K = -140.52 °C = -220.94 °F
- Critical pressure : 37.363 atm = 37.858 bar = 3.7858 MPa (MN/m 2 ) = 549.08 psi (=lbf /in 2 )
- Critical density: 10.448 mol/dm 3 = 302.6 kg/m 3 = 0.5871 slug/ft 3 = 18.89 lbm /ft 3
- Density (at 0°C and 1 bara): 1.276 kg/m 3 = 0.00248 slug/ft 3 = 0.0797 lb/ft 3
- Density (at 60°F and 1 atm): 1.208 kg/m 3 = 0.00234 slug/ft 3 = 0.0754 lb/ft 3
- Enthalpy (heat) of air at 0°C and 1 bara: 11.57 kJ/mol = 399.4 kJ/kg = 171.7 Btu(IT)/lb
- Entropy of air at 0°C and 1 bara: 0.1100 kJ/mol K = 3.796 kJ/kg K = 0.9067 Btu(IT)/lb °F
- Liquid density at boiling point and 1 bar: 875.50 kg/m 3 = 54.656 lb/ft 3
- Molar mass: 28.9647 g/mol
- Specific heatcapacity (Cp ) air at 0°C and 1 bara: 1.006 kJ/kgK = 0.24028 Btu(IT)/(lbm °F) or kcal/(kg K)
- Specific heatcapacity (Cv ) air at 0°C and 1 bara: 0.7171 kJ/kgK = 0.17128 Btu(IT)/(lbm °F) or kcal/(kg K)
- Thermal conductivity at 0°C and 1 bara: 24.35 mW/(m K) = 0.02094 kcal(IT)/(h m K) = 0.01407 Btu(IT)/(h ft °F)
- Thermal expansion coefficient at 0°C and 1 bara: 0.00369 1/K = 0.00205 1/°F
- Triple point pressure: 0.05196 atm = 0.05265 bar = 5265 Pa = 0.7636 psi (=lbf /in 2 )
- Triple point temperature: 59.75 K = -213.40 °C = -352.12 °F
- Viscosity, dynamic , at 0°C and 1 bara: 17.22 μPa s = 0.01722 cP = 0.3596x 10 -6 ( lbf s)/ft 2 = 11.57 x10 -6 lbm /(ft s)
- Viscosity, kinematic , at 0°C and 1 bara: 0.00001349 m 2 /s = 13.49 cSt = 0.0001452 ft 2 /s
Follow the links below to get values for the listed properties of air at varying pressure and temperature :
- Density at varying pressure
- Density, specific weight and thermal expansion coefficient at varying temperature
- Diffusion coefficients of gases in excess of air
- Dynamic and kinematic viscosity
- Prandtl's number
- Properties at gas-liquid equilibrium condition
- Specific heat (heat capacity) at varying pressure
- Specific heat (heat capacity) at varying temperature
- Thermal conductivity
- Thermal diffusivity
Air is a mixture of gases at standard conditions. However, at low temperature and high pressures the gas mixture becomes a liquid. The phase diagram for air shows the phase behavior with changes in temperature and pressure. The curve between the triple point and the critical point shows the air boiling point with changes in pressure.
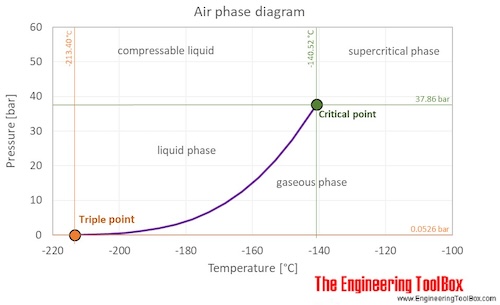
At the critical point there is no change of state when pressure is increased or if heat is added.
The triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
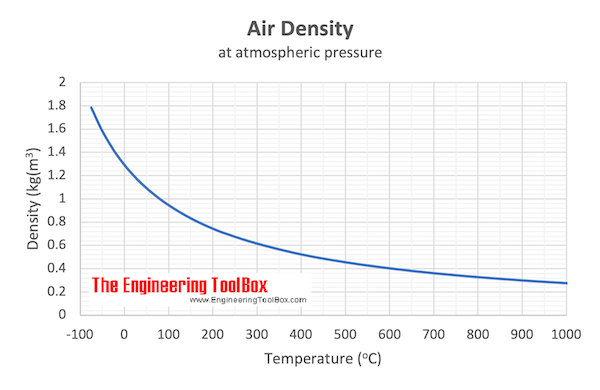
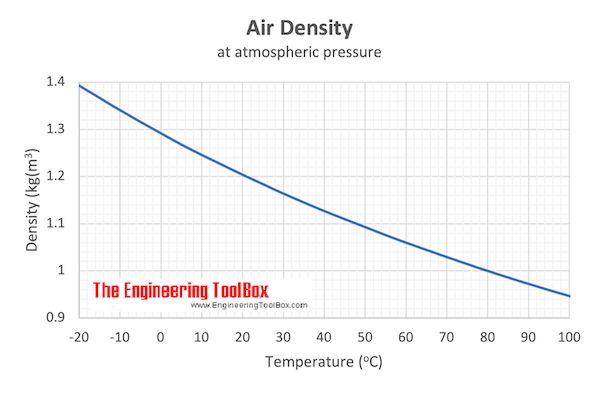
Example - Mass of Air at Temperature 100 o C
From the table above - the density of air is 0.946 kg/m 3 at 100 o C . The mass of 10 m 3 air can be calculated as
= (10 m 3 ) (0.946 kg/m 3 )
ρ = density (kg/m 3 )
Example - Mass of Air at Temperature 20 o C
From the table above - the density of air is 1.205 kg/m 3 at 20 o C . The mass of 10 m 3 air can be calculated as
m = (10 m 3 ) (1.205 kg/m 3 )
Example - Lifting Force of a Hot Air Balloon
An air balloon with volume 10 m 3 is heated to 100 o C . The temperature of the surrounding air is 20 o C. The change in gravity force (weight) of the air volume is the potential lifting force of the balloon. The lifting force can be calculated as
= (10 m 3 ) [(1.205 kg/m 3 ) - (0.946 kg/m 3 )] (9.81 m/s 2 )
F l = lifting force - change in gravity force (weight) (N)
dm = V d ρ = change of mass in the balloon (kg)
dρ = change in density due to temperature difference (kg/m 3 )




